| 20th C. BC |  Early Semitic The known beginning of the early Semitic alphabet is used in Egypt and Sinai penninsula. |  Wadi El-Hhol The oldest early Semitic script is inscibed on rock in Wadi-El-Hhol, Egypt. | |||
| 19th C. BC | |||||
| 18th C. BC | |||||
| 17th C. BC |  The Patriarchs The patriarchs, Abraham, Isaac and Jacob, the first recorded Hebrews, who lived in Canaan. | ||||
| 16th C. BC | |||||
| 15th C. BC |  Siniatic The early Semitic script is inscribed on rocks at Serabit El-Kadim. | ||||
| 14th C. BC | |||||
| 13th C. BC |  Middle Semitic The early Semitic alphabet evolves into the middle Semitic alphabet, also called paleo-Hebrew. | ||||
| 12th C. BC |  Moses The Israelites leave Egypt. | ||||
| 11th C. BC |  Tel Zayit This abecedary is inscribed using the middle Semitic script. | ||||
| 10th C. BC |  Greek Alphabet The middle Semitic alphabet is adopted by the Greeks. |  Gezer calendar Inscribed using the middle Semitic script. | |||
| 9th C. BC |  King David Rules over the southern kingdom of Judah. |  Greek The Greek alphabet evolves into the more modern form. |  Mesha Stele Also called the Moabite stone, is inscribed using the middle Semitic script. 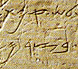 Siloam Inscription Inscribed in Hezekiah's tunnel with the middle Semitic script.  Tel Dan Inscription The inscription, which mentions the "house of David," is inscribed using the middle Semitic script. | ||
| 8th C. BC |  Israel Captured The northern Kingdom of Israel is captured by the Assyrians and the Israelites are taken into captivity (720 BC). |  Roman Romans adopt the Greek alphabet. |  Ketef-Hinom Scrolls Small silver scrolls, inscribed with the Aaronic blessing and other prayers, are inscirbed using the middle Semitic script and placed in a tomb at Ketef Hinnom in Israel. | ||
| 7th C. BC |  Lachish Ostraca The Lachish inscriptions are inscribed using the middle Semitic script. | ||||
| 6th C. BC |  Judah Captured The southern Kingdom is captured by the Babylonians and the Jews are taken into captivity (586 BC).  Judah Returns The Jews return to Israel from Babylon and rebuild the temple (516). | 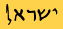 Late Semitic The middle Semitic script evolves into the late Semitic script, also called the Square Aramaic script. |  Sarcaphogus The Phoenician Sarcophagus in Sidon is inscribed using the middle Semitic script. | ||
| 5th C. BC | |||||
| 4th C. BC |  Septuagint Jewish scholars translate the Torah, the first five books of Moses, into Greek. | ||||
| 3rd C. BC |  Nash Papyrus Written in Egypt using the late Semitic script. | ||||
| 2nd C. BC |  Dead Sea Scrolls The first of the Dead Sea Scrolls are written, mostly in the late Semitic script, but some are written in the middle Semitic script. | ||||
| 1st C. BC | |||||
| 1st C. AD |  Temple destroyed The second temple in Jerusalem is destroyed by the Romans (70 AD). |  Targum Onkelos The Torah is translated into Aramaic by Onkelos, a Roman convert to Judaism.  Targum Jonathon The Prophets are translated into Aramaic by Jonathon Ben Uziel, a student of Hillel the Elder. | |||
| 2nd C. AD |  Jewish Revolt Revolt ends in failure and the Jewish people are expelled from the land of Israel. The Hebrew language ceases as their native language (135 AD). |  Bar Kockba letters The letters from General Simon Bar Kockba, during the second Jewish revolt against Rome, were written using the late Hebrew script (135 AD). |  Septuagint The writings and the prophets were translated into Greek by unknown translators. | ||
| 3rd C. AD |  Talmud The Talmud is written in the Late Semitic script. |  Peshitta The Hebrew Bible and the New Testament are translated into Aramaic. | |||
| 4th C. AD | |||||
| 5th C. AD |  Vulgate A Latin translation by Jerome of the Hebrew Bible and the New Testament. | ||||
| 6th C. AD | |||||
| 7th C. AD |  English English language adopts the Roman alphabet. | ||||
| 8th C. AD | |||||
| 9th C. AD | |||||
| 10th C. AD | 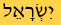 Modern Semitic The development of the vowel pointings that are inserted into the text to represent vowel sounds. |  Aleppo Codex The oldest known Hebrew Bible, is written with the modern Hebrew script by Jewish Masorites. | |||
| 11th C. AD | |||||
| 12th C. AD | |||||
| 13th C. AD | |||||
| 14th C. AD | |||||
| 15th C. AD |  Gutenburg Bible The first Bible, a copy of the Latin Vulgate, printed on moveable type. | ||||
| 16th C. AD | |||||
| 17th C. AD |  King James Bible English translation of the Bible published.(1611). | ||||
| 18th C. AD | |||||
| 19th C. AD |  Eliezer Ben-Yehuda Begins a revival of the Hebrew language for the Jewish people. | ||||
| 20th C. AD |  Nation of Isarel The state of Israel is established and Hebrew becomes the official language of Israel (1948). |

Ancient Hebrew Timeline |

Like what you’re discovering? Continue the journey from Bible reader to translator.
|